
Bitcoin, as a decentralized digital currency, has gained significant popularity over the years. However, one of the challenges associated with its use is the issue of double spending. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of what double spending is, how it affects Bitcoin transactions, and the measures taken to prevent it.

Double spending refers to the act of spending the same amount of digital currency more than once. In the context of Bitcoin, this means that a user attempts to spend the same Bitcoin transaction output (TXO) twice, which is essentially a form of fraud. This is possible because Bitcoin transactions are recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, and the currency is not centrally controlled.
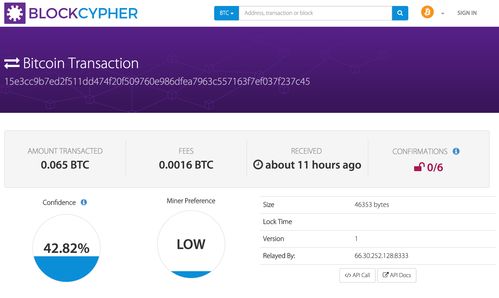
In Bitcoin, each transaction involves the transfer of a certain amount of Bitcoin from one address to another. When a transaction is made, the sender's Bitcoin wallet creates a new transaction that includes the recipient's address and the amount to be transferred. This transaction is then broadcast to the network and added to the blockchain.
However, before the transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it can be spent again. This is because the blockchain confirmation process takes time, and during this period, the sender can attempt to create another transaction using the same Bitcoin output. This is where the concept of double spending arises.
Double spending poses several risks to the integrity of the Bitcoin network and its users:
Loss of Trust: Double spending can erode the trust in the Bitcoin network, as users may become hesitant to accept Bitcoin as a reliable form of payment.
Financial Loss: Users who fall victim to double spending may lose their Bitcoin, as the sender can effectively steal the funds.
Network Congestion: Double spending can lead to network congestion, as the blockchain must process multiple transactions involving the same Bitcoin output.
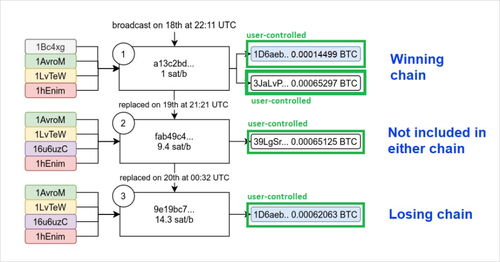
Several measures have been implemented to prevent double spending in Bitcoin:
1. Confirmation Time
One of the primary ways to prevent double spending is by waiting for a sufficient number of confirmations on the blockchain. A confirmation is when a new block is added to the blockchain, and the transaction is considered secure. Generally, six confirmations are considered sufficient to ensure the transaction is irreversible and not subject to double spending.
2. Lock Time
Bitcoin allows users to set a lock time for their transactions. This lock time specifies the number of blocks that must be mined before the Bitcoin can be spent again. By setting a lock time, users can prevent double spending by ensuring that the Bitcoin is locked for a certain period, making it impossible to spend it elsewhere.
3. CoinJoin
CoinJoin is a technique that combines multiple Bitcoin transactions into a single transaction, making it difficult to trace the individual inputs. This can help prevent double spending by obscuring the origin of the Bitcoin being spent, making it harder for the sender to create another transaction using the same inputs.
4. Segregated Witness (SegWit)
SegWit is a soft fork implemented in Bitcoin that improves the scalability and efficiency of the network. It also helps in preventing double spending by allowing more transactions to be included in a single block, reducing the window of opportunity for double spending.
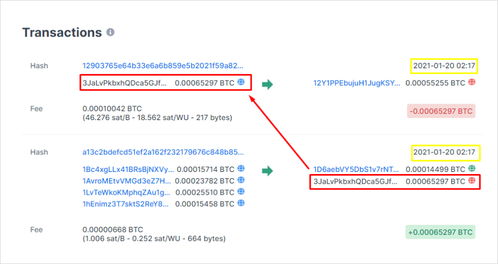
Double spending is a significant challenge in the Bitcoin ecosystem, but it is not insurmountable. By understanding the nature of double spending and implementing the necessary measures, the Bitcoin network can continue to evolve and maintain its integrity. As the technology advances, new solutions may emerge to further mitigate the risks associated with double spending, ensuring a more secure and reliable digital currency.
